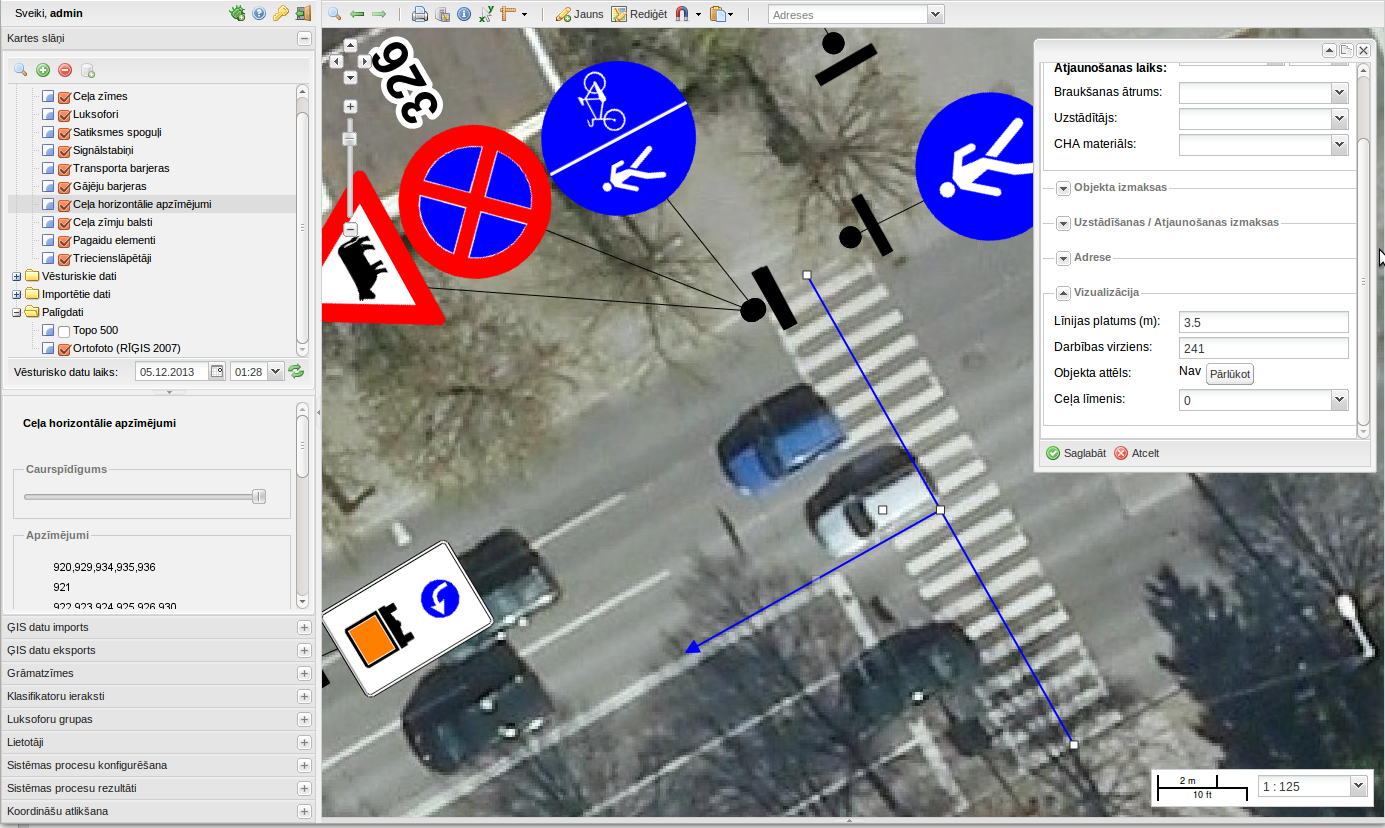

As almost every field of life, GIS can help in achieving excellence in transportation as well. It significantly aids in planning, monitoring and managing complex systems involved in transportation planning and management more effectively. GIS helps in determining capacity enhancements, improving operations, and identifying the most strategic investments for keeping the transportation system in any country running optimally. Let’s understand how we can use GIS in transportation for better management of road infrastructure.
The use of GIS in transportation is widespread. The major areas of applications include highway maintenance, traffic modeling, accident analysis, and route planning.
Highway maintenance management is a critical issue, which can be better harnessed using GIS . Authorities in many developed countries now actively use GIS for highways and transport management, mainly due to the benefits of falling costs and increasing ease.
The most important objective of using GIS is visualization achieved through maps . With visualization of real-time data, transport planners can easily identify potential issues that can be addressed more efficiently and economically than with the prevailing methods. Through detailed GIS maps, this information can be easily conveyed to decision-makers and the public.
For instance, Esri’s mobile GIS technology allows transportation maintenance and inspection crews to save time when collecting and updating information from remote locations. By using GPS and GIS-enabled devices, field crews accurately collect information from the field and seamlessly update corporate databases located in the office in real time. Through GPS and Esri technology, officials can track resources and assets in real time, allowing a quick response to any event that requires immediate attention. They can also more effectively manage mobile resources by instantly seeing the location of any work or inspection crew on a map , then redeploy resources as needed. Significant productivity gains are achievable by optimizing scheduling and routing maintenance and inspection teams, which not only boosts productivity but also results in significant fuel savings. The integration of work order management system, routing, and scheduling software allows modern highway managers to more efficiently direct their mobile workforces and ensure that resources are most effectively utilized.
 GIS in traffic modeling
GIS in traffic modelingGIS data can also be transformed into functional road models for large-scale traffic simulation. GIS data can model road networks around the world as polylines with attributes. Roadmaps from the GIS database can be extrapolated to automatically create geometrically correct and topologically consistent 3D models of large-scale road networks to be readily used in a real-time traffic simulation, interactive visualization of the virtual world, and autonomous vehicle navigation. The resulting model representation could also provide important road features for traffic simulations, including smoothly connected ramps, highways, overpasses, legal merge zones, and intersections.
Traffic accidents are one of the more important national and international issues, and their consequences are important for the political, economic and social level in a country. Management of traffic accident information requires information systems with analytical and accessibility capabilities to spatial and descriptive data. GIS delivers powerful spatial analytics, allowing the authorities to discover patterns and gain intelligence to better understand travel behaviors and perform accident analysis.
GIS significantly helps in accident analysis and leads to a reduction in the number of accidents on roads as well. GIS allows a more careful and accurate data selection, screening and reduction. Also, it allows a spatial analysis of the results in pre and post-processing. It allows the development of spatial statistics that rely on geographically-referenced data.
For instance, through the analysis of accident history, a transportation firm is able to identify significant safety issues and determine areas where measures can be taken to reduce the number of incidents. GIS can also allow the user to choose two months of accidents for comparison. The statistics can be useful in displaying a decrease in accidents over a period of time.
Route planning is an important application within transportation. Hurdles on routes can lead to unnecessary delays and losses. It is in favor of all businesses and people to know in advance which route is the best to follow. This knowledge can help in saving time and essentially gaining the best cost/benefit ratio. GIS-based systems quickly provide and analyze essential economic, demographic and cost estimates for planning new routes. It helps in analyzing existing routes, collecting data and informing the riders of change to routes.
Route planning is also applied as a part of location planning, analyzing catchment areas for different sites, calculating overall drive-times to and from the site, maximizing potential customer inflow and ensuring best possible accessibility.
Managing modern roadways is a complex affair. From computerized traffic control systems and incident and safety management systems to effective capital improvement planning and maintenance activities, transportation planners must draw on a wide array of technologies to effectively manage today’s roadways. GIS can help transportation planners to integrate agency-wide information to achieve better operational efficiencies and results. By bringing in GIS in transportation, higher efficiency can be achieved in the entire the infrastructure lifecycle—from planning and design through survey and construction management to operations and maintenance. GIS helps in mitigating woes, both for the travelers and the planners. As the travelers get to know about the best routes for their destinations, transportation professionals get equipped with enhanced ability to manage their infrastructure.